surgical
pearls
Managing Floppy Iris
Syndrome
Use of
Flomax has been tied to this complication.
By
Jerry Helzner, Senior Editor
David F. Chang, M.D., and John R.
Campbell, M.D., have recently identified a new small-pupil
syndrome they've named Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome
(IFIS). They've tied it to use of Flomax, the most commonly
prescribed alpha-adrenergic blocker for the treatment of
benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH).
IFIS during cataract surgery is
characterized by: iris billowing in response to normal
irrigating fluid currents; a strong tendency toward iris
prolapse; and progressive miosis during the phaco and cortical
irrigation/aspiration (I/A) steps.
In this article, we'll provide
several pearls that surgeons should consider when confronted
with a potential IFIS case.
|
|
|
|
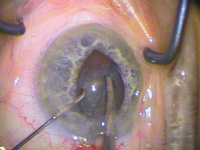
IFIS is
characterized by iris billowing, prolapse to phaco and
side port incisions, and progressive miosis during
phaco.
|
|
Mitigating IFIS
Dr. Chang offers the following
surgical pearls for preventing or mitigating IFIS:
"If the pupil dilates poorly
preoperatively, you should specifically ask about prior Flomax
use. Even if it has been stopped for 1 to 2 years, IFIS can
still occur, indicating that there must be some permanent
change to the iris dilator muscle. Some urologists prescribe
Flomax for urinary retention symptoms in women, and
predictably, IFIS has been encountered in female Flomax
patients.
"It is not clear whether other
nonsubtype-specific alpha-1 blockers cause IFIS. While the
IFIS patients in our two studies were all on Flomax, a few
anecdotal reports note IFIS in patients on Hytrin, Cardura,
and Uroxatrol.
"Several features of IFIS increase
the risk of complications for an unsuspecting and uninformed
surgeon. First, if the pupil is small, commonly used
mechanical stretching techniques, with or without partial
thickness sphincterotomies, are ineffective in maintaining an
adequate pupil diameter. Furthermore, some IFIS pupils dilate
quite well, or expand well enough following viscoelastic
injection to make the capsulorhexis step quite
straightforward. It is not until hydrodissection and phaco
that the problems of IFIS suddenly and unexpectedly
occur.
"We reported increased
retrospective posterior capsule rupture rates with IFIS, and
believe that the unanticipated cascade of iris misbehavior was
the likely explanation.
"A number of different approaches
have been tried with varying success. Stopping the Flomax for
1 to 2 weeks seems to permit wider dilation in some eyes, but
doesn't alone prevent IFIS.
"Dr. Sam Masket feels that stronger
cycloplegia, such as with atropine, may help. Dr. Dick
Lindstrom feels that supracapsular phaco is a helpful
technique, wherein the prolapsed and tilted nucleus keeps the
pupil from constricting all the way down. Drs. Bob Osher and
Doug Koch rely on Healon5 (see below). "I have found that the
tighter 1.2-mm incisions of bimanual microincisional phaco are
of some help in preventing iris prolapse.
"I believe that all of these
strategies work much better if the iris dilates reasonably
well to begin with, and are less effective if the pupil is
already small. In that case, the best strategy is to employ
iris retractors in a diamond configuration as described by Dr.
Tom Oetting. Although this increases the cost and surgical
time, it assures a safe-sized pupil opening throughout the
case. Pupil expansion rings are another option, but can be
more difficult to insert if the chamber is shallow, or the
pupil is small."
Using Healon5
To safely and effectively manage
the challenges of IFIS, Robert H. Osher, M.D., uses his
slow-motion phaco technique and Healon5.
In slow-motion phaco, vacuum,
aspiration and infusion are carefully managed. After an
initial vacuum of 250 mmHg to burrow into the lens, vacuum and
aspiration rates are kept lower than normal, which allows a
lower infusion rate and fosters stability.
The viscosity and space occupation
properties of Healon5 make it ideal for use with this
technique, Dr. Osher says.
"First, viscomydriasis with Healon5
allows me to create an adequate capsulorhexis without iris
prolapsing to the wound," he explains.
"During nucleus chopping and
removal, not only does the slow-motion phaco preserve the
Healon5 in the anterior chamber, it deters the floppy iris
from 'leaping' into the phaco tip, even though the pupil may
get smaller. I have also learned how to remove cortex without
disturbing the OVD, still keeping the floppy iris from
leaping."
|
|
|
|
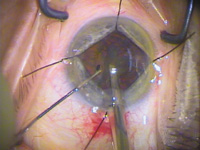
Disposable
iris retractors placed in a diamond configuration in
IFIS patient. Subincisional retractor is placed through
a separate stab incision just posterior to the phaco
incision.
|
|
For removal of the Healon5, Dr.
Osher places the I/A tip under the IOL, directs the port
toward the single-piece acrylic IOL, and with several seconds
of high vacuum, evacuates the viscoelastic from the capsular
bag. To complete the evacuation, he places the tip in the
anterior chamber with the port toward the cornea.
Before he removes the irrigating
tip, he puts the 27-gauge cannula through the stab incision
and holds it against the optic. He injects Miochol as the I/A
tip is being withdrawn.
"This maneuver keeps the chamber
from abruptly shallowing because the Healon5 effectively masks
positive pressure," Dr. Osher says. "The iris prolapse is
retarded by the deeper chamber into which the pupil rapidly
constricts from the Miochol."
Dr. Osher has performed
phacoemulsification on approximately a dozen patients with
IFIS, and says, "I have not had to rely on either iris hooks
or a mechanical device for pupil dilation."
Multicenter Study
Started
"We don't really know whether IFIS
will be associated with a higher rate of cataract surgical
complications now that ophthalmologists can foresee and
anticipate the problem," says Dr Chang. "For this reason,
we've started a multicenter prospective study to assess what
the complication rate of IFIS will be, as long as the surgeon
is prepared and able to use alternative pupil management
strategies such as those we describe. We plan to enroll up to
150 consecutive Flomax patients at 11 sites across the
country."